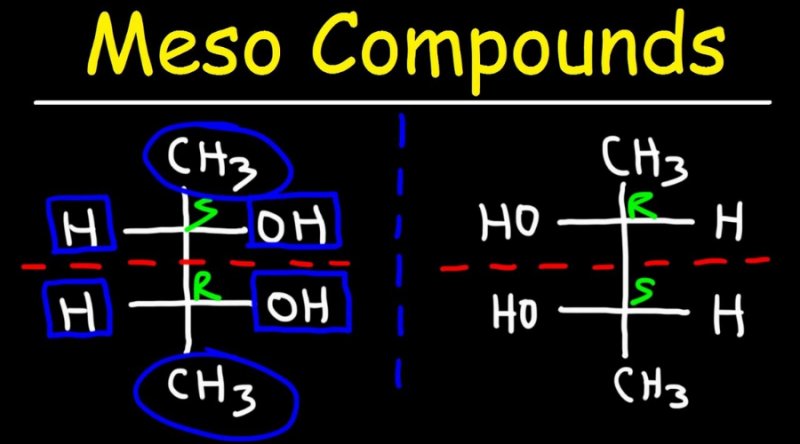
Meso compounds are achiral compounds with chiral centers. Even though a meso compound has two or more stereocenters, its internal plane of symmetry makes it impossible to superimpose its mirror image and makes it optically inactive.
As a result of an internal plane of symmetry, a meso compound has two or more chiral centers but no optical activity. Compounds with zero net rotation of plane polarised light are called mesomers. A mesomer is an organic molecule with two identical chiral carbons, which results in zero net rotation.
Meso Compound Definition
In addition to having several chiral centers, meso compounds are also achiral substances. Despite having stereocenters, it is optically inactive since it is overlaid on its mirror counterpart.
It is called a meso compound if its achiral center is chiral. Despite having two or more stereocenters, meso compounds have an internal plane of symmetry that makes them optically inactive on their mirror images.
The term meso compound or meso isomer refers to a non-optically active member of a group of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. Despite having two or more stereogenic centers, the molecule is not chiral.
Meso Compound Examples
Despite their chiral centers (sp3 hybridised tetrahedral atoms bound to four distinct groups), meso compounds are generally achiral. Meso compounds should include at least two chiral sp 3 hybridised atoms, except for the nitrogen atom of tertiary amines, and at least one internal plane splitting the molecule into two mirror images.
It is impossible for the molecule to be planar due to the presence of tetrahedral centers. Compounds with even one symmetry element are achiral, which means they cannot rotate plane-polarised light! Consequently, meso compounds are not optically active.
Despite its plane of symmetry (the horizontal plane passing through the red broken line), this meso complex has two chiral carbons.
Meso Compound is Optically Active
Meso compounds or meso isomers are stereoisomers that are not optically active, but that have at least two optically active stereoisomers. The molecule is not chiral even though it has two or more stereogenic centers. A chiral compound has several chiral centers, meaning it is an achiral compound. Although it has stereo centers, it is optically inactive, as it is overlaid on its mirror image.
The compound is split in two by an internal symmetry plane. Via the inner mirror, the two sides reflect one another. If the molecule is divided into two symmetrical sides by an internal plane, the stereochemistry of the left and right sides should be opposite. This means the stereochemistry of the stereocenter can be “cancelled out.” Therefore, the result is optically inactive. Meso molecules can also be cyclic molecules theoretically. Meso compounds do not exhibit optical activity because optical activity cancels out in the presence of symmetry planes.
Frequently Asked Questions on Meso Compound
Why is meso achiral?
Meso compounds are achiral since they have a plane of symmetry, which will produce a mirror image that cannot exist in the original molecule.
Are achiral compounds always meso?
In spite of whether a molecule has a chiral center or not, meso compounds contain a plane of symmetry and are therefore achiral. It is a plane of symmetry that divides molecules into two halves, each of which is a mirror image of the other.
How do you know if a compound is optically active?
A compound that can rotate optically is said to be optically active. An optically active compound is a chiral compound. There are four atoms or groups attached to the carbon in the chiral compound, which contains an asymmetric center. Two mirror images are formed that cannot be superimposed.
What is meso compound in organic chemistry?
Meso compounds or meso isomers are non-optically active members of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. In other words, even though the molecule contains two or more stereogenic centers, it is not chiral.
What is the meaning of meso form?
When dextrogyrates and levogyrates are balanced in a structure against each other, the element cannot demonstrate optical activity