In today’s fast-paced and highly competitive markets, the ability to innovate swiftly and accurately is crucial for businesses seeking to gain an edge. Enter rapid prototyping — a revolutionary process that blends speed and precision, fundamentally changing how products are designed and brought to market. Whether in aerospace, automotive, healthcare, or consumer electronics, rapid prototyping has transformed industries by enabling engineers, designers, and manufacturers to quickly produce prototypes, test ideas, and iterate designs with unparalleled efficiency. This article dives into the game-changing impact of rapid prototyping, exploring its role, benefits, and the technologies driving it forward.
The Importance of Speed in Prototyping
In product development, time is often a critical factor. The ability to quickly create and test a prototype can make the difference between beating competitors to market or falling behind. Rapid prototyping drastically shortens the development cycle by enabling fast iteration. Rather than waiting for tooling, casting, or other lengthy processes involved in traditional manufacturing, Rapid Prototyping allows engineers to make changes to a design and see the results immediately.
For instance, in industries like consumer electronics, where products have short life cycles, quick time-to-market is essential. Rapid prototyping allows designers to test the feasibility of a design and validate form, fit, and function early in the process. This, in turn, reduces the risk of costly errors further down the line, ensuring that products can be launched quickly and with confidence.
Precision: Why Accuracy Matters
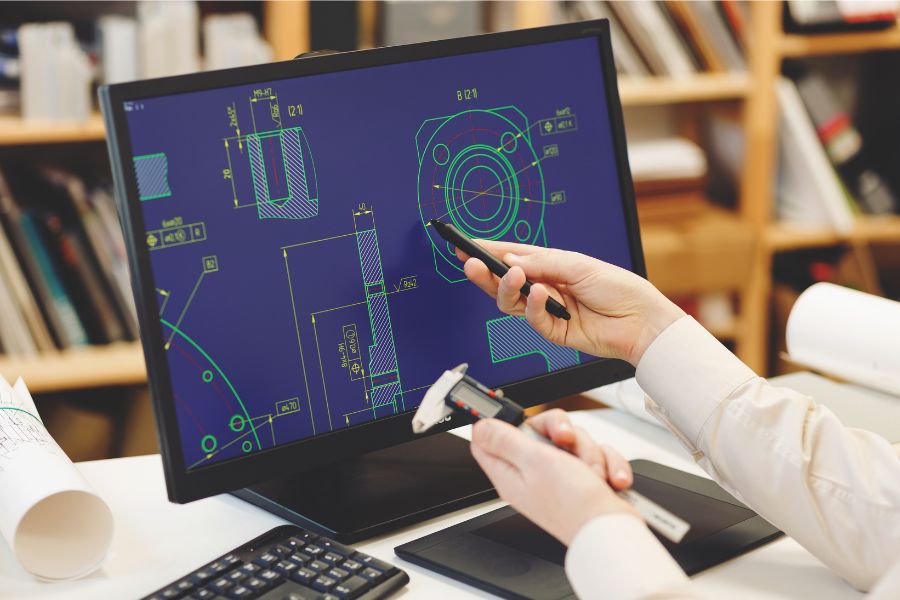
While speed is a major benefit, the precision that rapid prototyping offers is equally game-changing. Modern prototyping technologies allow for highly accurate models, even for complex geometries and intricate designs. This level of precision is crucial in industries such as aerospace and healthcare, where exact measurements and tolerances are non-negotiable.
For example, in medical device development, where even minor errors can have significant consequences, rapid prototyping ensures that prototypes are produced with exact specifications. Similarly, in aerospace, where safety and performance are critical, precision prototypes allow engineers to test components with a high degree of accuracy before final production.
Types of Rapid Prototyping Technologies
Several technologies enable rapid prototyping, each offering unique benefits depending on the application:
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing): 3D printing is one of the most popular forms of rapid prototyping. It builds prototypes layer by layer, allowing for the creation of complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible with traditional manufacturing. Materials such as plastics, metals, and resins can be used, providing flexibility in the design process.
CNC Machining: CNC machining involves the removal of material from a solid block to create a prototype. This method is known for its high precision and ability to work with a variety of materials, including metals. CNC machining is often used when a high degree of accuracy is required or when creating functional prototypes that need to undergo stress testing.
Laser Cutting: Laser cutting is another rapid prototyping technology, particularly useful for creating detailed, flat components or parts. This method is commonly used in industries like electronics and textiles, where fine details and precision are required.